GPS:
--°
--.---' North
---°
--.---' East
Area: ~70,000
sq. meters
Maximum length:
~550 m
Maximum depth: 22 m
Class: Meromictic
Brief Description
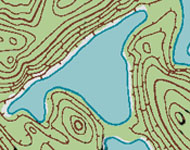
Big Crocodile Lake (BCL) is the largest of the meromictic marine lakes.
It is also one of the most remote, set in the heart of Mecherchar with
no direct access. High ridges surround the lake except at three points:
at the western tip (left, in picture) where it is most easily accessed,
at the northeastern tip where it is separated by a low limestone platform
from an L-shaped lake, and at its southern end where a 50 m thick band
of mangrove leads to Crocodile Hole. Crocodile Hole may have been joined
with BCL when the mangrove was less substantial, many centuries in the
past. Most probably, Big Crocodile Lake, Crocodile Hole, and even L-shaped
Lake were inter-connected by surface channels when sea-level was up to
5 meters higher during the Holocene. At times of much lower sea- and lake-level,
however, Big Crocodile Lake, Crocodile Hole, and L-shaped Lake all must
have been quite distinct, even more so than BCL and L-shaped Lake currently.
As such, these lakes likely have a reticulated evolutionary history, and
it is unclear what were the origins and what are the relationships of
animals that inhabit the lakes, such as the moon jellyfish (Aurelia
sp.). One thing is certain, the eponymous saltwater crocodiles can easily
move between these lakes, as well as others farther afield.
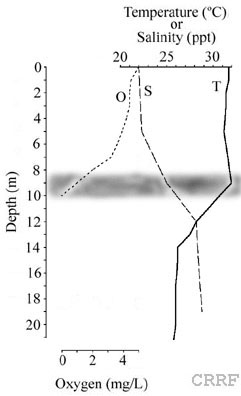
Legend:
O, oxygen
S, salinity
T, temperature
Horizontal shading indicates depth of chemocline.
(Redrawn from Hamner & Hamner 1998)
Species
List
Arthropoda:
Crustacea - Copepoda
Chlorophyta:
Chordata:
Teleostei - Acentrogobius janthinopterus, Sphaeramia orbicularis
Cnidaria:
Anthozoa - Entacmea
medusivora
Scyphozoa - Aurelia
sp.
Mollusca:
Bivalvia - Brachidontes sp.
Porifera:
Sources: CRRF unpubl. data; Fautin & Fitt 1991; Hamner & Hamner
1998; Dawson & Martin, unpubl. data